Building energy management systems, also known as BEMS, provide an efficient way to monitor and control energy usage and other functions in residential and commercial properties. A BEMS allows owners and facility managers to oversee key aspects of the building from heating and air conditioning to lighting and security.
Through automated controls and remote access capabilities, a BEMS helps optimize energy consumption. This reduces costs while maintaining occupant comfort levels. The system continuously tracks power usage and adapts settings like thermostats and lighting levels based on preset conditions.
For homes, a BEMS gives residents control over HVAC, appliances, and more from any internet-connected device. Commercial systems offer additional features for managing multiple zones, equipment, and tenant spaces across large facilities. Both deliver cost and operational benefits through centralized automated control.
Illustration of a home energy management system
Buildings use a significant amount of energy each year. In the European Union (EU), buildings account for around 40% of total energy consumption on average.
The situation is even more important to address in developing countries, where many buildings are less efficient. In 2003, all the carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from the EU-25 countries totaled 3.8 million tonnes. Of that, 12%, or 479 million tonnes came from households.
In the United Kingdom specifically, buildings are responsible for about 28% of CO2 emissions. Within that, space heating contributes 53% of building emissions, lighting/appliances is 22%, and water heating is 20%. Cooking only makes up 5%.
To help efficiently manage a building’s functions, Building Energy Management Systems (BEMS) are used. BEMS help control things like heating, ventilation, air conditioning (HVAC), lighting, fire alarms, security, and maintenance. They allow the smooth operation of the building.
The International Energy Agency (IEA) defines a BEMS as “an electrical control and monitoring system that can control monitoring points and an operator terminal.” BEMS uses computers and small processors to watch, store data, and share information about a building. Other common names for this tech are Building Management System (BMS) and Energy Management System (EMS).
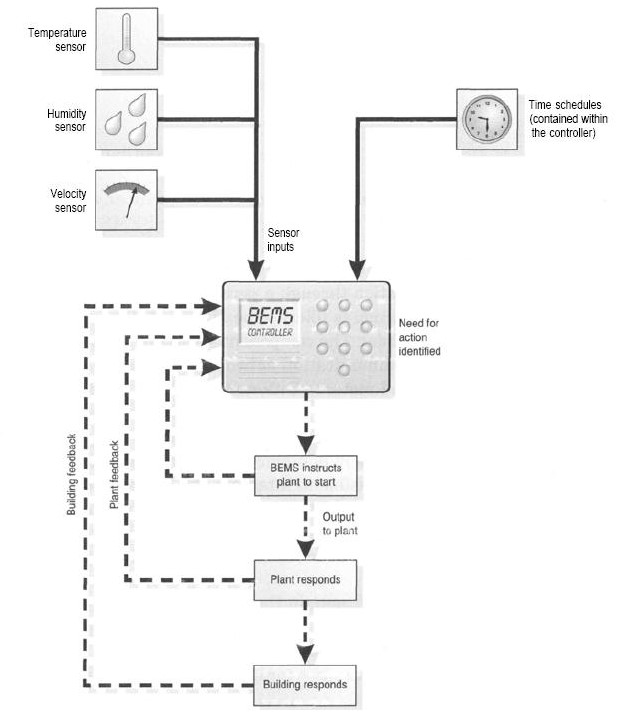
While all buildings need some type of control, a BEMS offers more advanced control. A key part is communication – a BEMS can send and receive data from all over a building to one central control unit. This allows the operator to make choices to save energy. For example, if parts of a building are empty, the central unit can lower the heat there.
Feasibility of technology and operational necessities
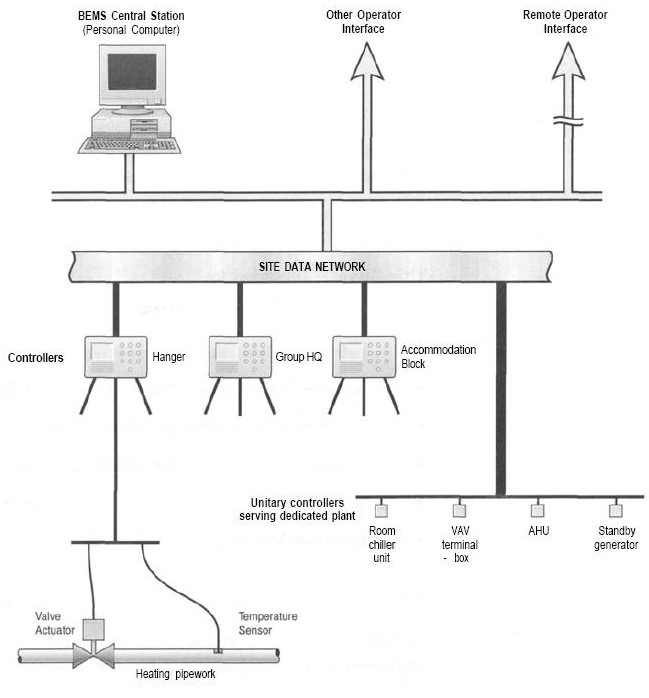
All BEMS systems have some basic parts to make them work. One of the most important is called the principal operator position. This is sometimes called the central station too. It’s where the whole system is controlled from.
The principal position is connected to smaller controllers in different areas, like different floors of a building. These smaller controllers are called remote outstations. They can either run on their own or take orders from the principal position.
Most BEMS connect all these parts using the internet. This allows quick and easy communication between the main control room and the remote outstations all over the building.
From the principal position, the operator can see what the remote controllers are doing. They have an interface that shows everything. Using this, the operator can change settings on the outstations if needed.
For example, the BEMS provider may limit control to just energy-saving functions. Or a customer could pay extra to also control security cameras and locks from the main control room. It all depends on what the building owner wants the system to do.
No matter what size the building is, these key parts of a principal operator position, remote controllers, and internet connection between them are what make a BEMS work.
A BEMS is meant to achieve three important goals for any building, according to research from the International Energy Agency (IEA) in 1997.
The first is providing a comfortable, healthy environment for people inside. Nobody wants to work or live somewhere with bad air quality or temperatures.
Secondly, the BEMS helps keep everyone safe. This means things like controlling security cameras, and alarms, and even making sure the heat and electricity keep working.
And third, it aims to make the building run efficiently so it saves money for the owner. Less wasted power means lower utility bills.
One of the big benefits of a BEMS is it can watch over many different parts of the building or group of buildings. Some common things it can adjust include heating, air conditioning, ventilation, lighting, hot water for showers or kitchens, how electricity is distributed, and total energy use.
It can even control elevators or escalators in big office towers. Having just one central system in charge of all these functions allows everything to work smoothly together.
The IPCC, or Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, reported in 2007 that commissioning is a very important part of setting up a successful BEMS system. Commissioning means checking the quality of all parts of the process, from the early design stages through installation.
It’s key to think about what the BEMS will need to do even when first drawing up the building plans. This is called considering the functions in the design. If you do that, the system can run much better and save more energy.
Rather than adding a BEMS later to an existing building, it’s smarter to build it into the original design. That way everything can be set up correctly from the beginning.
For example, if you know a BEMS will control elevators and escalators, the wiring and electronics for that can be included in the construction.
How the technology contribute to socio-economic development and environmental protection?

When used in big buildings like offices or factories, BEMS technology can help people in two important ways.
First, it makes the workplace safer. BEMS can find dangers like fires or security issues, and then tell emergency crews right away. It also lets workers know about problems to watch out for.
Second, it keeps the air and surroundings healthier. BEMS watches factors such as air quality, water quality, and more. If something gets too bad, like carbon monoxide rising to unsafe levels, it kicks in right away to fix it. This might mean turning on more fans to get fresh air moving.
In homes, BEMS is great for saving on bills and comfort too. It shows residents how much power they use so they can save more. The system also sets things like temperature so the place is always cozy. This extra info and control helps people feel better while spending less.
While BEMS is pretty easy to use with its touchscreens, installing and maintaining it takes training. Technicians need to learn how all the parts connect and work together. Operators also get taught how to run the whole system smoothly.
Less energy used means a more reliable supply too. With BEMS helping buildings need less power, we can build fewer new stations. It even cuts down on how much fuel we import from other places.
BEMS gives managers real-time details on energy use. This lets them spot ways to use power smarter. And the system itself saves energy by coordinating everything like lights and machines. Less use means less pollution too when power comes from coal.
For example, lights take a huge amount of electricity worldwide. BEMS can help here too by automatically turning them off when areas are empty for a bit.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Increased energy efficiency | Higher initial costs for design and installation |
| Improved environmental conditions | Operation and maintenance costs might be higher compared to simpler management systems. However, the BEMS is also capable of reducing overall costs through improved energy efficiency and more efficient use of staff |
| More efficient use of staff | Need for a skilled operator |
| Improved fire, security, and other emergency procedures | Requires commitment at all levels throughout its operational life to maintain maximum effectiveness |
| Improved standards of plant/building functioning | |
| Improved management of the building |
Clean Development Mechanism market status
Three methods can be useful for a project that wants to enter the CDM market.
- Energy efficiency and fuel switching measures for buildings (Version 10 AMS-II.E.): This methodology covers energy-saving measures at a single building or group of similar buildings. BEMS could qualify here if it saves energy through efficient appliances or layout in a complex or hotel.
- Energy efficiency and renewable energy measures in new housing (AMS-III.AE Version 1): This methodology applies to efficient design and renewable energy in new homes. A BEMS project for new apartments may be able to use this if the system leads to big energy reductions.
- Demand-side energy efficiency activities for specific technologies (Version 13 AMS-II.C.): This methodology focuses on encouraging efficient equipment like lights, fans, and air conditioners across many sites. A BEMS could fit here if it connects multiple buildings as one technology to manage things in an energy-saving way.
Last Words
In conclusion, Building Energy Management Systems or BEMS can help save big money and energy for homes and businesses alike. BEMS watches over important stuff like heat, lights and more to keep places comfortable while using less power. By installing one, a building will run smoother and be easier on the environment too. With BEMS technology, the future looks bright for cheaper bills and a cleaner world!