Flood hazard mapping is a critical resource for strategic land use in flood-prone areas. It generates concise, accessible maps and charts that highlight at-risk areas and guide mitigation and response efforts.
Such maps play a key role in increasing flood awareness among the general public, local authorities, and organizations. They encourage residents and businesses in vulnerable areas to investigate their specific flood risks and adopt appropriate safety measures.
It is important to consider the role of climate change in flood hazard mapping. These maps generally offer a static view of flood risk at a particular time.
With climate change effects like sea level rise and changes in storm intensity, the dynamics of flood risks are evolving, necessitating updates to these maps to reflect the changing vulnerabilities of regions to flooding.
Flood Hazard Map for Cairns, Australia
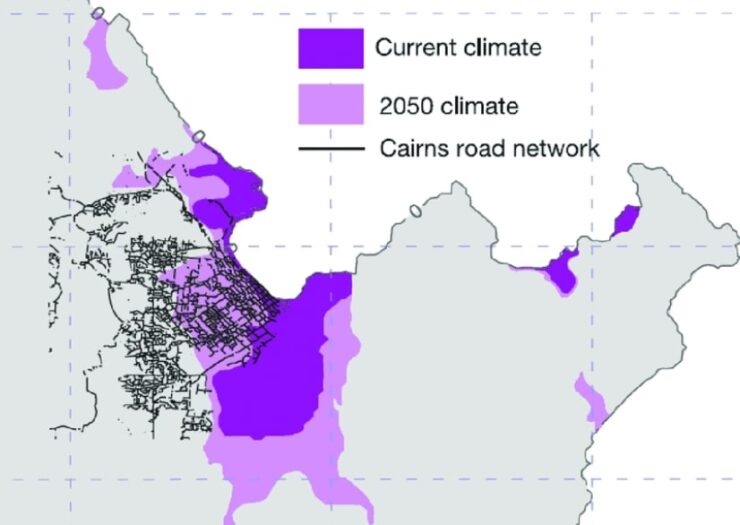
Given the impact of climate change and relative sea level adjustments, it’s crucial to periodically update flood hazard maps to accurately reflect the evolving flood risks. These updates should incorporate factors like relative sea level rise (RSLR), erosion, and changes in storm frequency and intensity.
Developers use these maps to evaluate flood risks in potential construction zones, while insurers rely on them to set flood insurance premiums where applicable.
Coastal flood forecasting often depends on complex numerical models due to the scarcity of empirical data and the rarity of extreme coastal events. These models simulate the processes and phenomena that contribute to coastal floods.
The determination of coastal flood hazards involves understanding how storm surges and waves interact with seabed bathymetry and coastal land cover, which influences how far inland flooding will reach. Therefore, coastal flood models need to consider these geographical and oceanographic features, along with the mechanics of storm surges and waves.
The development of flood maps typically merges topographic data with historical or modeled data on extreme sea levels and wave heights. This combination helps estimate the water level at the coast during extreme conditions and how it might extend inland, often utilizing storm surge and wave models.
It’s also important to consider the effectiveness of existing coastal defenses in these models, which helps predict when these defenses might be overtopped, leading to flooding.
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) are extensively used to produce flood hazard maps. They efficiently compile data from various maps and digital elevation models, enabling the calculation of flood extents by comparing local elevations with predicted extreme water levels.
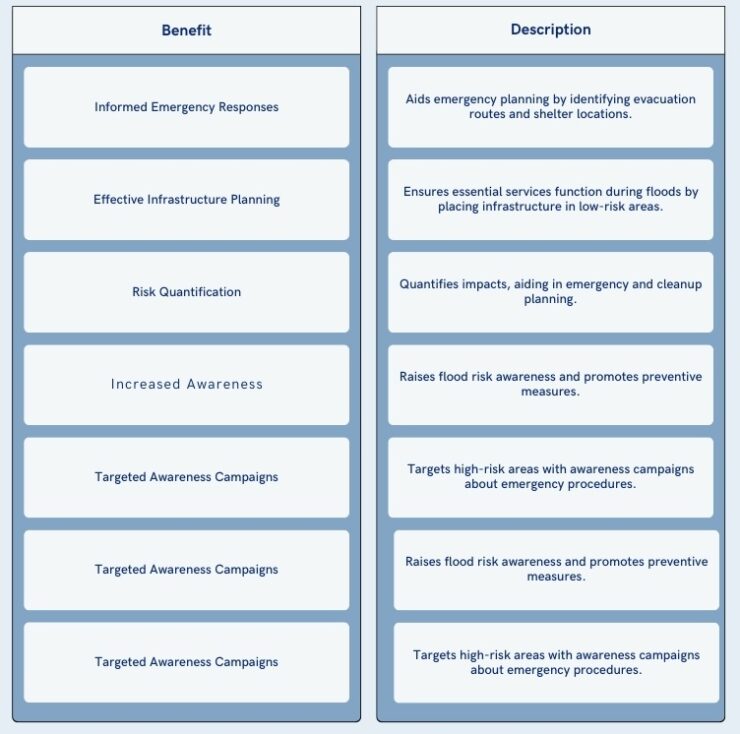
What are the Benefits?
Being aware of all the benefits of this approach is an absolute must.
Here are the most important ones:
Let’s Check the Disadvantages
While flood hazard mapping is a crucial tool for managing flood risk, it is not without its challenges.
Let’s check them out:

Financial Requirements and Costs
The costs of flood hazard mapping are not widely known. Therefore it is not possible to provide likely cost estimates here.
We provide a number of factors which are likely to contribute toward the cost of flood hazard mapping:
- External expertise on numerical modelling of flood risk brought in from academic institutions or commercial organisations
- Topographic surveys (LiDAR or remote sensing) to provide information on land elevation which will feed back into the flood risk model
- Historic costs of collecting extreme event data such as water levels, wave heights, etc.
- Cost of employing a Geographic Information System (GIS)
Institutional and Organisational Requirements

Flood hazard mapping may be difficult to undertake at the community level due to the need for complex numerical modelling for the forecast of extreme water levels, storm surges and wave heights.
The required expertise and modelling capacity is unlikely to be locally available, especially in developing countries. As such, it may be necessary to enlist the help of external organisations.
Following developed country examples, this type of mapping has been accomplished via national programmes.
Barriers to Implementation
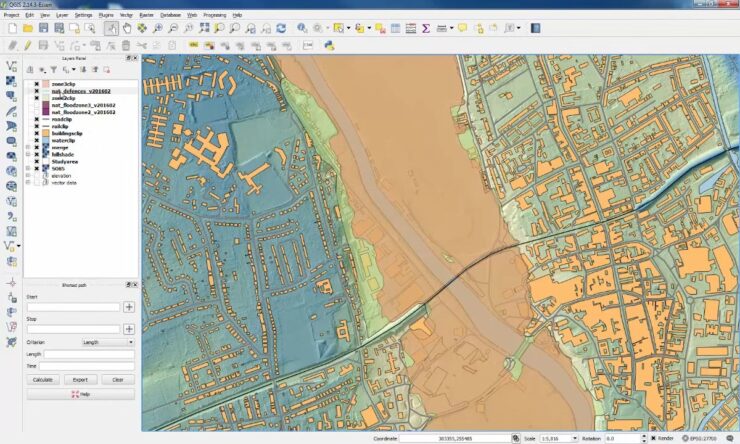
Flood hazard mapping depends on access to:
- Topographic data
- Records of long-term extreme events
- Sophisticated numerical modeling techniques
Implementing these requires specialized modeling skills and expertise that may not always be accessible.
If the public does not understand the advantages of flood hazard mapping, this lack of awareness can hinder its implementation.
People might favor allocating public funds towards more visible and immediate flood and erosion control measures instead of investing in flood hazard mapping.
Opportunities for Implementation
Flood hazard mapping complements and strengthens other adaptation options, such as flood-proofing measures, emergency planning, provision of flood shelters and evacuation planning. As such, this approach could be applied almost universally, irrespective of the other adaptation technologies that are used.







